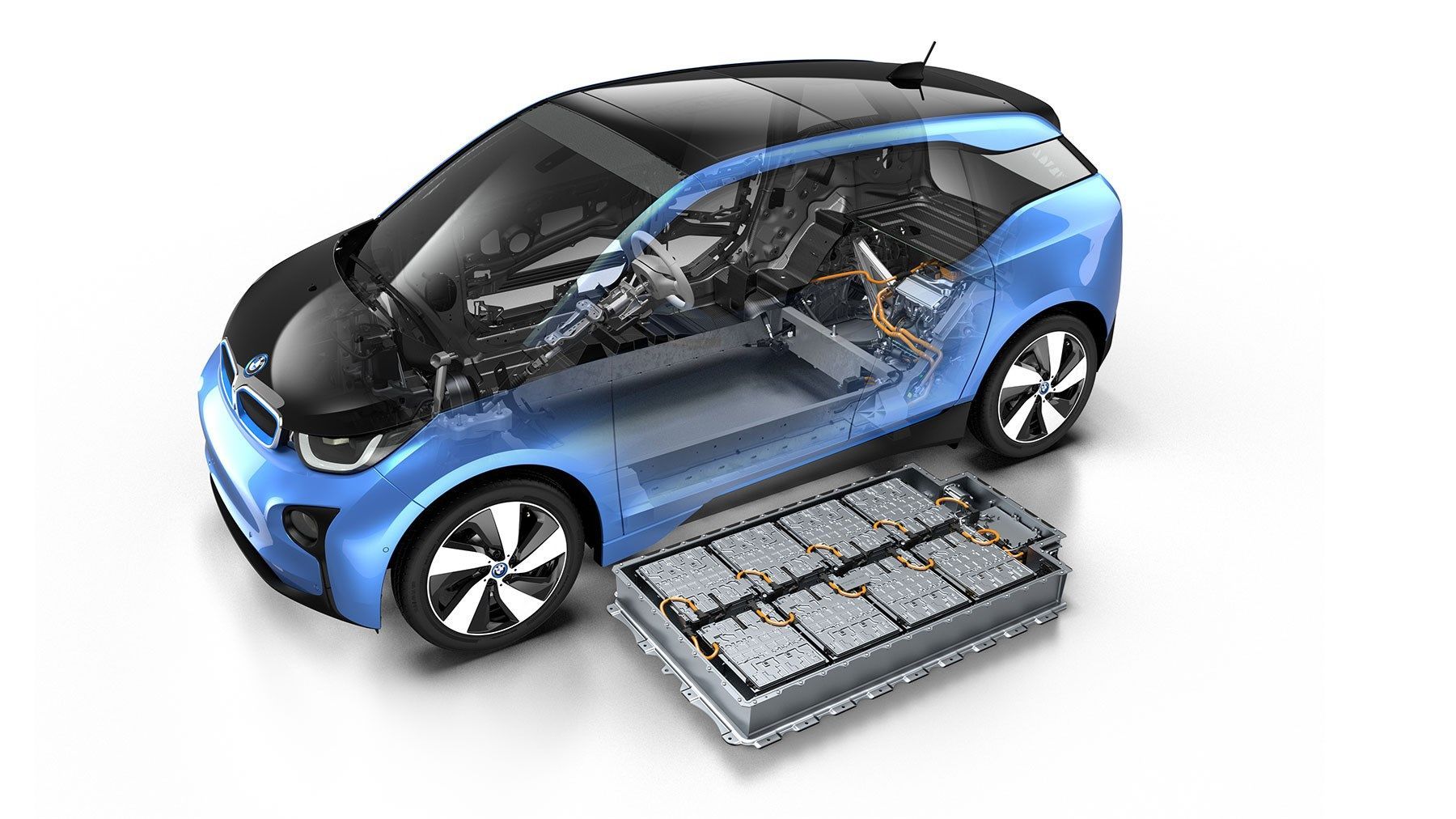
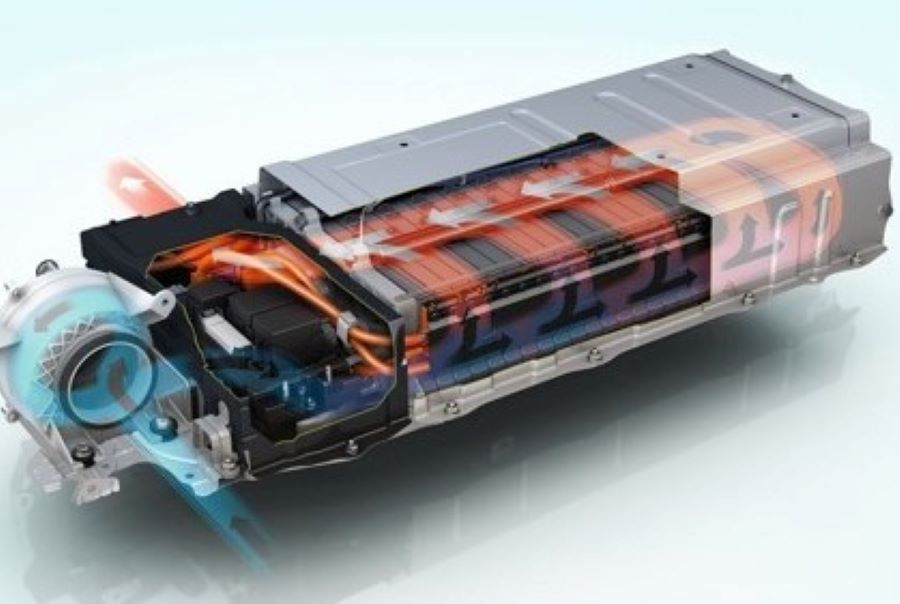
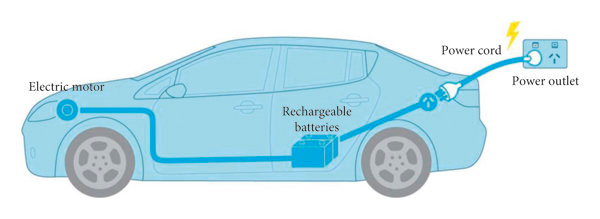
How do Electric Cars Work?
Electric cars use an electric motor powered by electricity stored in rechargeable batteries to propel the vehicle.
- The rechargeable batteries in electric cars are usually made of lithium-ion, similar to those found in laptops and smartphones.
- The batteries can be charged by plugging the car into an external power source, such as a home charging station or a public charging station. As the battery charges, the stored electrical energy is converted into chemical energy, which can be used to power the electric motor later.
- Electric cars offer a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, as they emit zero tailpipe emissions and require less maintenance due to their simpler drivetrain.
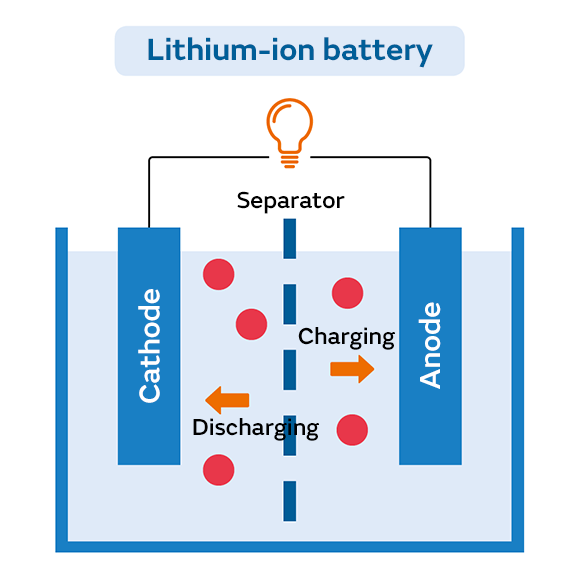
What is a Lithium-ion Battery?
- A lithium-ion battery in a car is a type of rechargeable battery that uses lithium ions to store electrical energy that is used to power the electric motor of an electric car.
- The lithium-ion battery pack is typically made up of hundreds or even thousands of individual cells, which are connected together to form a large battery pack.
- These batteries have a high energy density, which means they can store a lot of energy in a relatively small and lightweight package.
- They are also known for their high efficiency, long lifespan, and low self-discharge rate.
What technology is required in an Electric car?
- Electric Motor: to convert electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy that propels the car.
- Battery: to store electrical energy and provide power to the electric motor. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in electric cars due to their high energy density and long lifespan.
- Power Electronics: to manage the flow of electrical energy between the battery, electric motor, and other electrical components in the car.
- Onboard Charger: to convert AC power from an external power source, such as a home charging station or a public charging station, into DC power that can be used to charge the battery.
5. Regenerative Braking: to convert the kinetic energy of the moving car into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery for later use.
6. Thermal Management: to regulate the temperature of the battery pack and other electrical components to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance.
7. Control System: to manage and coordinate the operation of the various components in the car, including the electric motor, battery, and power electronics. It also includes a user interface, such as a dashboard display, to provide feedback to the driver about the car's performance and battery status.
Overall, electric cars require a complex integration of technologies to operate efficiently and reliably. As battery technology and other components continue to improve, electric cars are becoming increasingly practical and popular as a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
What infrastructure is required?
To support the widespread adoption of electric cars, several types of infrastructure are required, including:
- Charging Stations: Electric cars need to be charged regularly, which requires the installation of charging stations in public places, such as parking lots, shopping centers, and rest areas. Home charging stations can also be installed for personal use.
- Grid Infrastructure: The electricity grid needs to be upgraded and expanded to support the increased demand for electricity from electric cars. This includes the installation of new power generation and transmission capacity, as well as smart grid technologies to manage and optimize the flow of electricity.
- Battery Recycling Facilities: The growing number of electric cars on the road will lead to a significant increase in the number of used batteries that need to be recycled. Specialized recycling facilities are required to safely and efficiently recycle the batteries and recover valuable materials.
- Workforce Training: As the adoption of electric cars grows, a skilled workforce is needed to install and maintain the charging infrastructure, repair and maintain electric cars, and recycle batteries. Training programs and certifications can help to ensure that the workforce is prepared to meet these needs.
- Government Incentives: Governments can play a role in supporting the adoption of electric cars by providing incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and subsidies, to offset the higher upfront costs of electric cars and charging infrastructure.
Overall, the infrastructure required to support electric cars is complex and requires significant investment and planning. However, as the technology continues to improve and become more affordable, and as more infrastructure is put in place, electric cars are becoming an increasingly viable and attractive option for consumers and governments around the world.
Who is currently making Electric Cars?
There are several manufacturers of all-electric vehicles, and the number is growing rapidly as the demand for electric vehicles continues to increase. Some of the main manufacturers of all-electric vehicles include:

Tesla
Tesla is one of the most well-known manufacturers of electric vehicles, and they offer several models, including the Model S, Model X, Model 3, and Model Y.

Nissan
Nissan's all-electric vehicle is called the Nissan Leaf, which has been on the market since 2010.

Chevrolet
Chevrolet offers the Bolt EV, which has a range of over 250 miles on a single charge.

Ford
Ford offers the Mustang Mach-E, which is an electric SUV with a range of up to 300 miles.
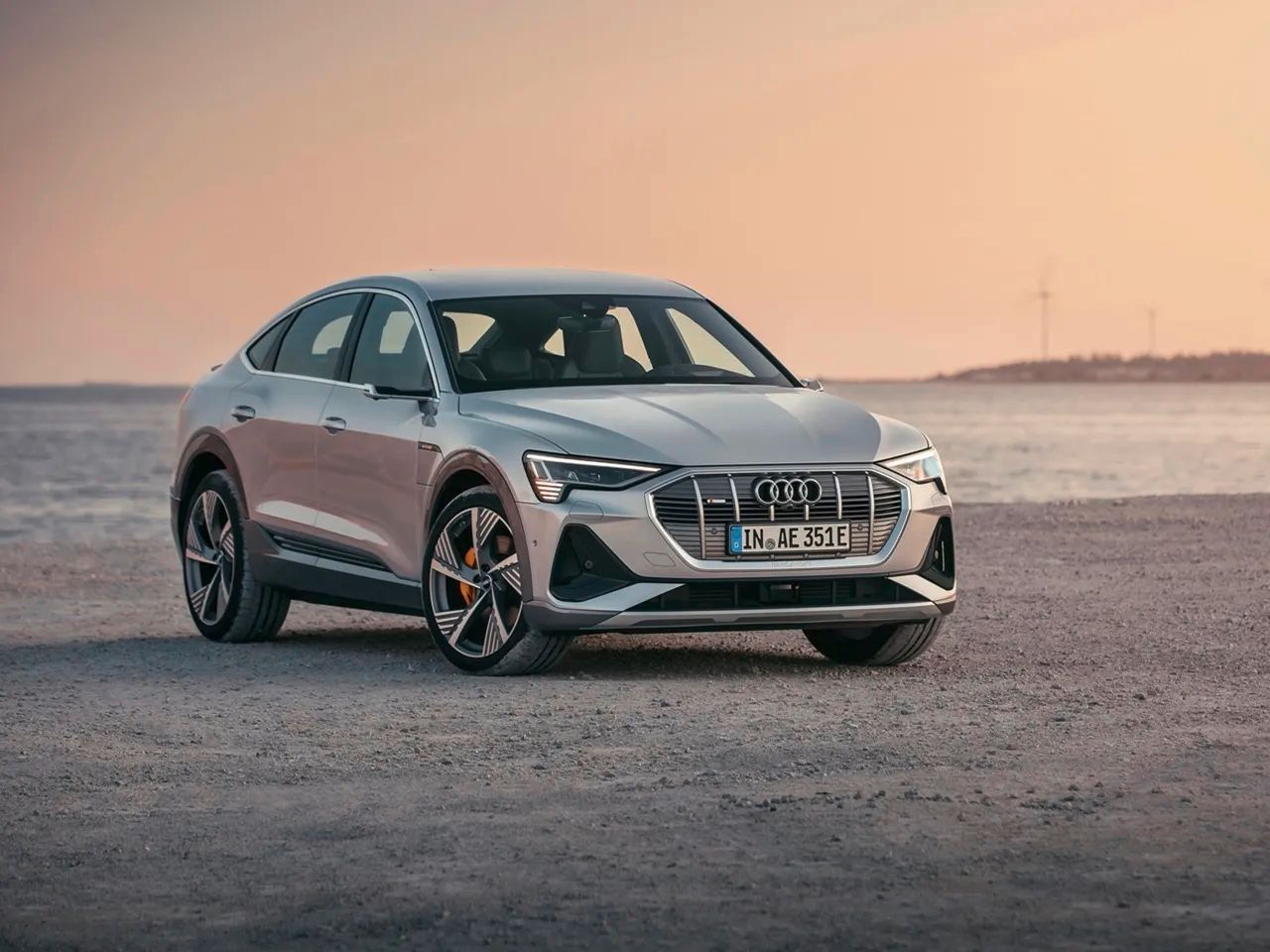

Audi
Audi's all-electric SUV is called the e-Tron, and they also offer a Sportback version of the vehicle.

Volkswagen
Volkswagen offers the ID.4, which is an electric SUV with a range of up to 250 miles.
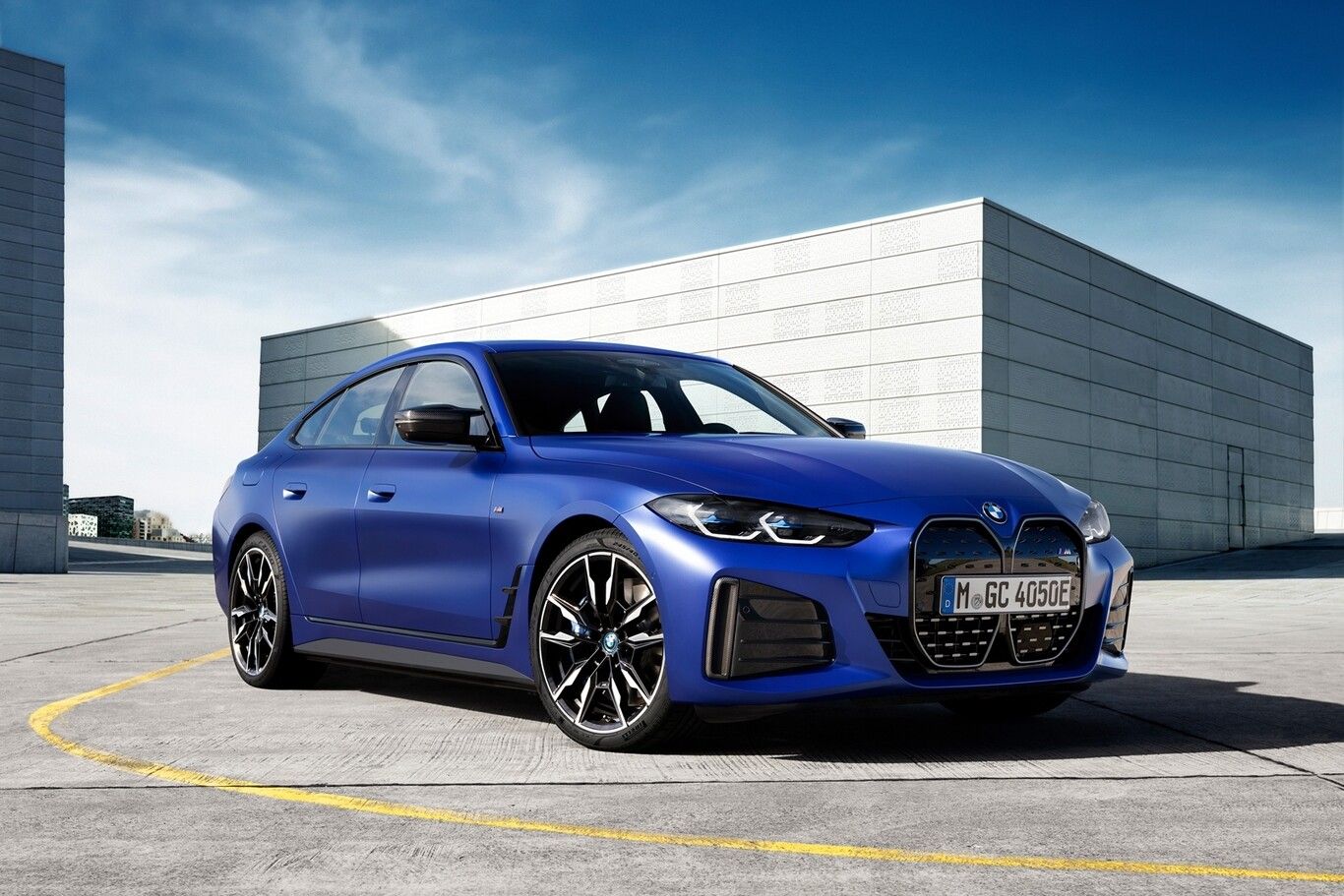

BMW
BMW offers the i4, which is a compact electric vehicle with a range of up to 365 miles on a single charge.
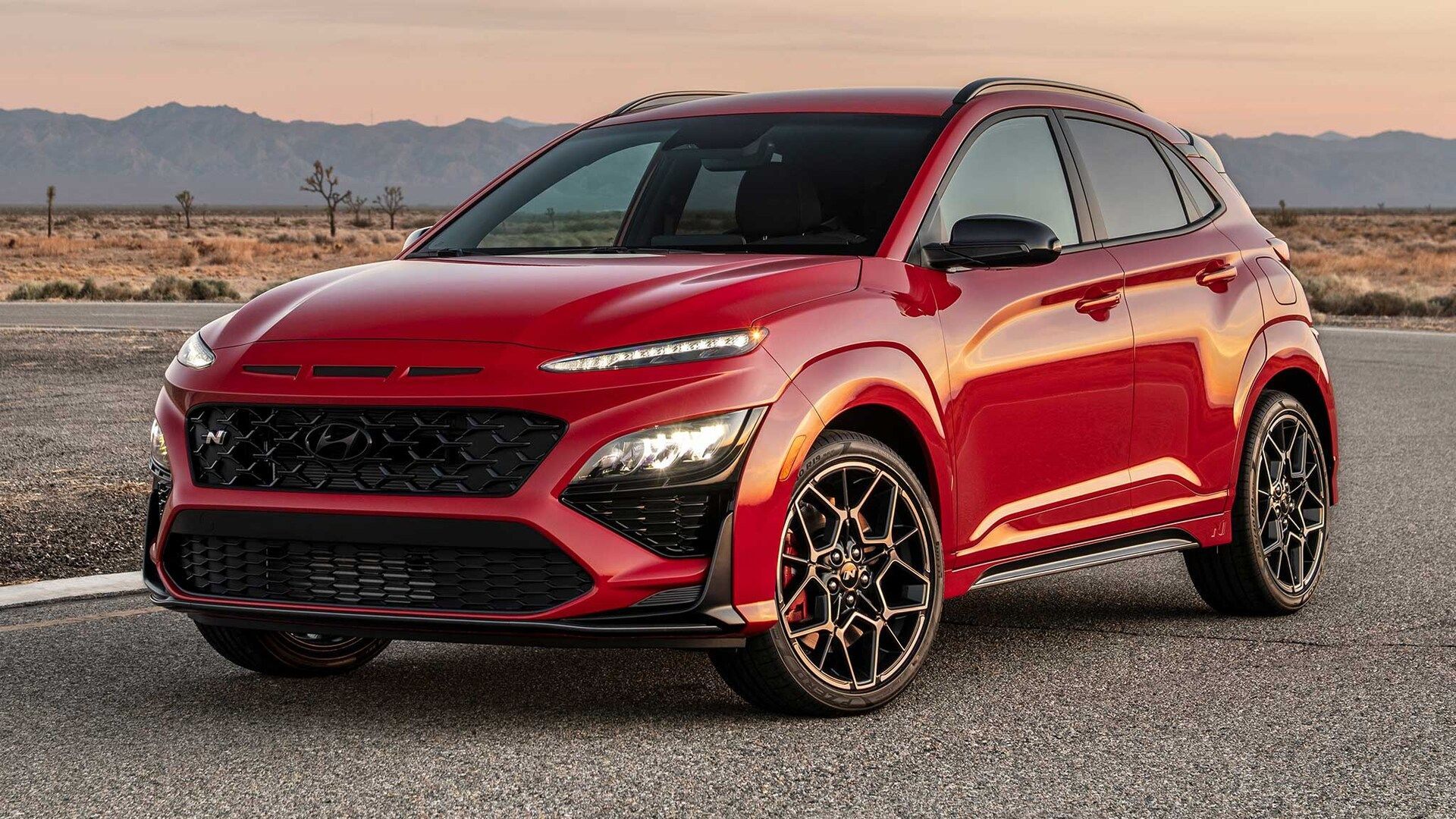

Hyundai
Hyundai offers the Kona Electric, which has a range of up to 258 miles on a single charge.
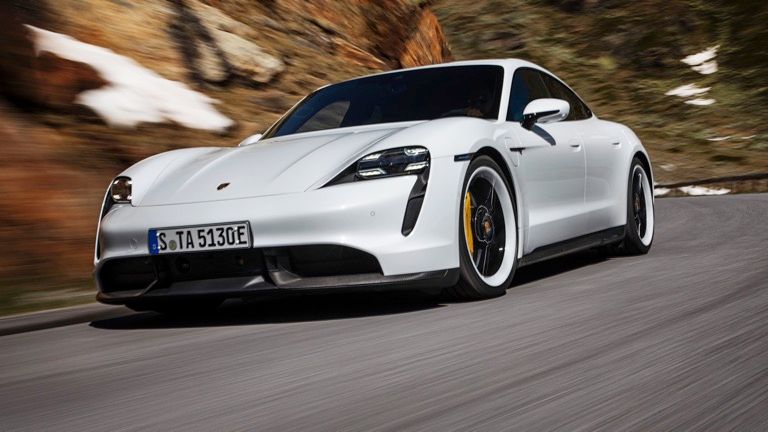

Porsche
Porsche offers the Taycan, which is an all-electric sports car with a range of up to 227 miles on a single charge.